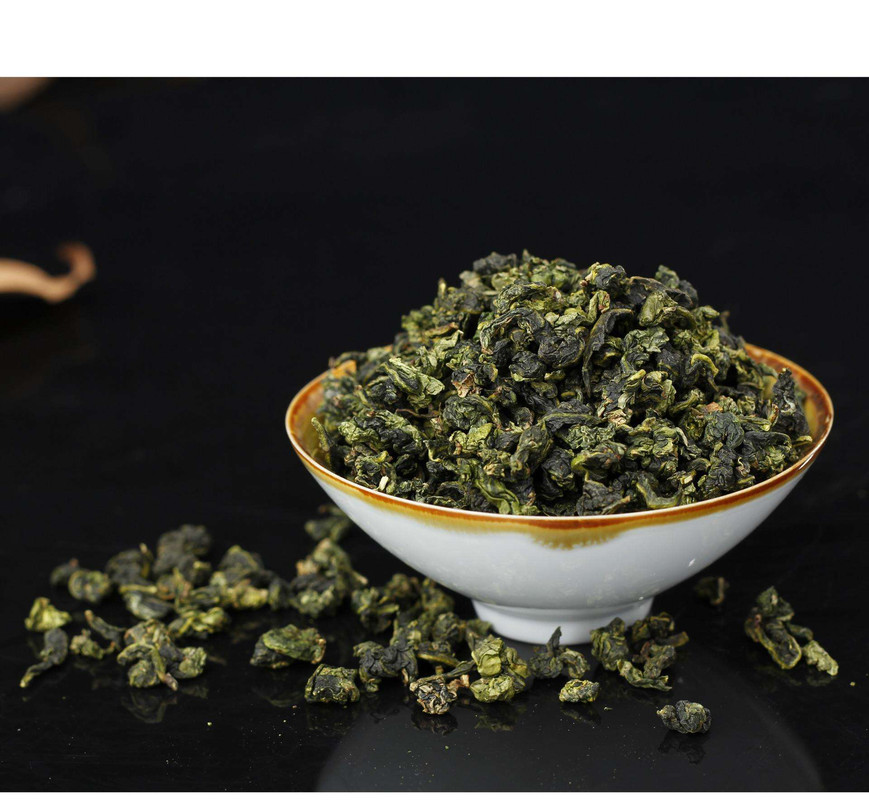
Oolong tea, also known as Wu Long tea, occupies a unique niche in the vast tapestry of tea varieties worldwide. Hailing from China, particularly the Fujian and Guangdong provinces, as well as Taiwan, oolong tea is renowned for its complex flavor profile that lies somewhere between green and black teas. This distinction is attributed to its semi-oxidation process, where tea leaves undergo partial fermentation, resulting in a tea that is neither fully oxidized like black tea nor unoxidized like green tea. Here, we delve into the intricate process of cultivating oolong tea.

Soil and Climate Conditions
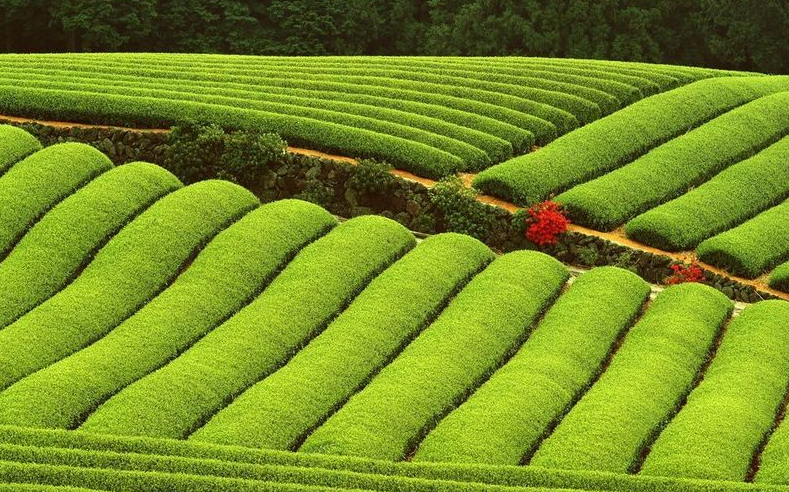
The ideal growing environment for oolong tea begins with the soil. These tea plants thrive in well-drained, acidic soils rich in organic matter. The terrain should offer good drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other diseases. In terms of climate, oolong tea plants prefer a subtropical to temperate climate with mild winters and warm, humid summers. Adequate rainfall, preferably evenly distributed throughout the year, is crucial for sustaining healthy growth. Morning sunlight followed by afternoon shade is ideal, as it balances photosynthesis with protection from intense UV rays.
Propagation and Planting
Propagation of oolong tea plants is typically done through vegetative methods such as cuttings or grafting, as these methods preserve the desired characteristics of the parent plant more reliably than seed propagation. Cuttings are taken from healthy, mature plants during the dormant season and then planted in nurseries. Once the cuttings have rooted and grown sufficiently, they are transplanted to the main tea fields.
Planting density is another critical factor. Too many plants can lead to competition for nutrients and sunlight, while too few can result in underutilization of land. Proper spacing ensures that each plant receives adequate sunlight and air circulation, promoting healthy growth and disease resistance.
Pruning and Training
Pruning is a vital aspect of tea plant maintenance, particularly for oolong tea, which benefits from a well-structured canopy. Regular pruning encourages the plant to produce new, tender shoots, which are the preferred material for making high-quality tea. The pruning process also involves training the plant to form a bushy shape, making it easier to harvest leaves uniformly.
Harvesting Techniques
Harvesting oolong tea leaves is a delicate task requiring skill and precision. The best leaves for oolong tea are the two youngest leaves and the bud, known as ‘two leaves and a bud.’ These are picked by hand, usually early in the morning when the leaves are at their freshest and contain the highest concentration of flavor compounds. Harvesting is a seasonal activity, with peak periods varying depending on the region and climate.
Processing Oolong Tea
The semi-oxidation process that defines oolong tea begins immediately after harvesting. The leaves are withered to reduce moisture content, then shaken or tumbled to initiate oxidation. This shaking or tumbling process is repeated several times over a period of several hours to days, allowing for controlled oxidation. The degree of oxidation can vary greatly, from around 10-15% for lighter oolongs to 50% or more for darker varieties. After oxidation, the leaves are fixed by heating to stop the process and preserve the desired flavor profile.
Flavor Profile and Health Benefits
Oolong tea’s flavor is characterized by its complexity and variety, ranging from floral and fruity notes in lighter varieties to earthier, roasted flavors in darker ones. This versatility makes oolong tea appealing to a wide range of tea enthusiasts.
Beyond its taste, oolong tea is valued for its potential health benefits. Like other teas, it contains antioxidants such as catechins and polyphenols, which may help reduce inflammation, support cardiovascular health, and aid in weight management. Some studies suggest that oolong tea, due to its unique processing, may offer particular benefits in improving insulin sensitivity and promoting fat metabolism.
Conclusion
Cultivating oolong tea is an art form that combines precision agriculture with centuries-old tradition. From meticulously selecting the right soil and climate to carefully managing the plant’s growth and harvest, each step contributes to the production of this highly esteemed beverage. The semi-oxidation process that gives oolong tea its distinctive flavors and health benefits underscores the importance of skill and patience in tea production. As the world continues to appreciate the nuances of oolong tea, the art of its cultivation remains a vital part of preserving and celebrating tea culture.